This article is about method statement of quality control of civil related work and project.
CIVIL RELATED QUALITY CONTROL METHOD STATEMENT
1. Introduction
The proposed system of Quality Control and testing is generally as per Contract Specifications; PCI, ACI and Royal Commission, SADARA , SAUDI ARAMCO , Petrofac ,SABIC, MA’ADEN and SEC and in line with ISO 9001-2008. All relevant facilities and personnel for Quality Control or precast elements to be supplied to the Project are existing and as indicated in this document. Responsibility for Quality Control lies with an experienced and qualified Quality Control Manager, with fully qualified inspecting Engineers and Supervisor reporting to him.
Quality Control Supervisor has the authority to correct formworks, reinforcing steel arrangement and/or shall reject finished units, should it/they fail to show compliance with the Specification requirements.
2. Principle factors in quality control
Many factors enter into the Control of Quality of Precast and Pre-stressed elements. The most important requirements for production control are:
1. Qualified Personnel responsible for designing detailed, production, inspection and erection.
2. Clear and complete shop drawings.
3. Adequate monitoring, inspection and testing.
4. Proper proportioning and mixing of concrete.
5. Control of dimensions and tolerances, including proper formwork and/or mould construction.
6. Proper fabrication, bending, placement and securing of reinforcement.
7. Proper handling, placing, consolidation and protection of concrete.
8. Proper finishing procedures.
9. Timely and continuous curing.
10. Proper mould/formwork stripping procedures.
11. Proper handling, storing, loading, transporting, erection of elements.
12. Routine inspection and checking of all operations, for full compliance of above all.
Quality control shall have direct lines of communication to engineering, production, Quality Control and management with responsibility only to reporting to management.
Responsibilities shall include:
a) Inspection and verification of the accuracy of dimension of units, quantity, supports, spacers and location of reinforcement and cast in items, form and mould layout and other matters pertaining specifically to Quality in production. Checking adequacy of the form to produce units without displacement, distortion or surface defects.
b) Monitoring, inspection and observation of all tightening and/or stressing operations to ensure that specified procedures are used.
c) Regular inspection of concrete proportioning, batching, mixing, handling, placing consolidation, finishing and protection.
d) Checking propriety of materials, embedment, sleeves, recesses, etc and mixtures, proportioning a mix, evaluating it in relation to both design and production Quality requirements and if necessary modifying it to obtain the desired finish in the end product.
e) Fabrication of representative trial samples and testing.
g) Appearance (finish) inspection as necessary to ensure that units have a uniform finish, color, shape, thickness, dimension, quality and matching the appearance of approved specimen samples.
f) Inspection of all finished products for conformance with shop drawings and Specifications. This conformance must be within specified tolerances that are applicable to each unit or element produced for the Project work and are within the limits of the standard.
APPLICABLE STANDARDS
• ACI “American Concrete Institute”
• PCI MNL 117 “Manual of Quality Control for Architectural Precast Concrete”
• PCI MNL 116 “Manual of Quality Control for Structural Precast Concrete”
• ASTM “American Society for Testing and Materials”
• BSI “British Standards Institution”
3. Inspection of Casting Works
The forms are inspected before each casting being checked against approved shop drawings in respect of the following:
Dimension of form work or mould, and Quality of mould itself, like
• Recesses.
• Concrete cover.
• Length.
• Width.
• Depth.
• Block-outs.
• Deflection.
• Bow.
Cleanliness and correct oiling of form.
Type, position of embeds and quantities.
• Lifting sockets
• Fixing sockets
• Electrical conduits
• Sleeves
Correctness, position of reinforcement and quantities.
• Rebar type and size
• Rebar length and hook
• Rebar spacing
• Rebar support.
4. Inspection during casting
Regular checks are made that full consolidation and/or compaction of concrete is being achieved in the correct manner either by vibrator motors air operated or poker vibrators air operator and that the location of reinforcement and embedment are not unduly disturbed.
The following procedure shall be done during casting:
a. Checking slump as per ASTM C143 for each set of concrete samples, prior to collecting specimen for comp. strength test as per the ASTM C 94.
b. Checking Concrete Temperature of concrete batched at each pour time recorded
c. Making 4 cylinder specimens for each mix to test on daily basis; minimum cylinder to test is 1 cylinder at 3 days, 1 cylinder at 7 days and 2 cylinders at 28 days.
d. Checking air content as per ASTM C231 in case air entrained admixture is used.
e. Recording Unit weight and yield.
5. Curing and Protection
For Curing Compound
• The curing compound will be sprayed on the concrete surface using a sprayer pump as specified in the data sheet.
• After the demoulding, same procedure will be applied for the bottom face of the hardened concrete.
• The curing compound should be applied uniformly on the concrete surface to form an even film thin layer preventing the moisture loss and improving the cement hydration.
For Water Curing
• Water curing shall be continuous for 7 days after casting.
• Max. TDS in water used for curing shall not exceed 1 OOOPPM.
• The saturated burlaps shall be covered with plasticized sheet.
For Steam Curing
• The maximum curing temperature shall not exceed 180°F (82°C).
• Insulated tarpaulins are effectively use for a combination of moisture and heat retention .
• Steam curing is usually used for Pre-stressed units like Hollow Core Slabs and Double Tee Slab.
Finishes
• Conformance with approved samples.
• Inspection of superficial repair work.
• Application of sealer I water proofing agent, in case it is required.
No precast concrete unit may be dispatch without approval from QC stockyard inspector.
6. Inspection after demoulding (post casting)
After demoulding and removal to stockyard, each precast element is checked against any variance with respect to approved details via shop drawings in respect of the following:
4.1 Dimension
• Length
• Width
• Depth
• Block outs
• Deflection
• Bow
• Recesses
• Concrete cover.
7. Batching Plant Inspection
Regularly on daily basis and at random time inspections of the batching plant shall be carried out to ascertain the following:
• Correct materials usage, quantity and type, per approved fab mix (design mix) is prepared for the work.
• Batch plant is functioning correctly and that recommended minimum mixing times are being adhered to, and that correct mixing procedure is used.
• Batch plant equipment shall be calibrated by independent test lab at every four months interval, maximum.
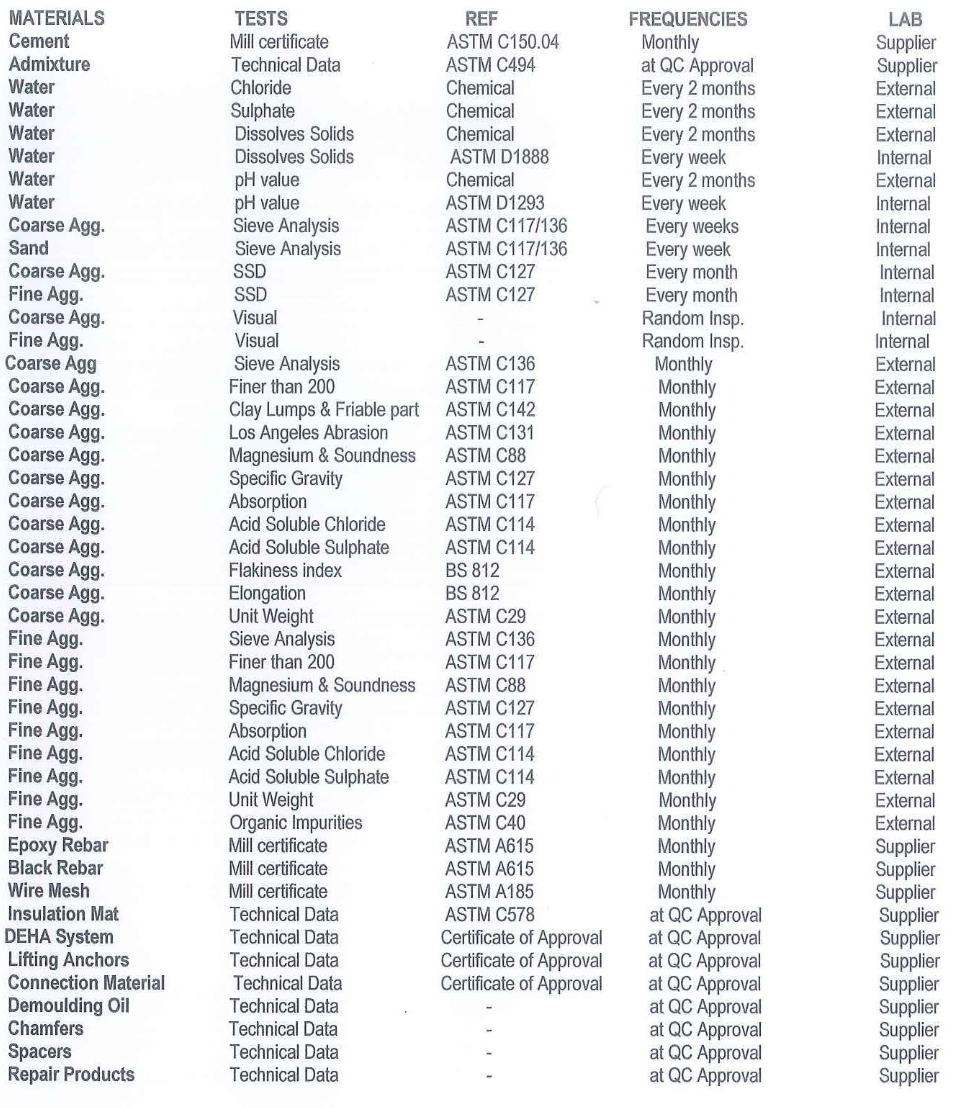
8. Inspection of Materials
The following materials shall be used in Quality production of the Elements and are tested according to Specification referenced above, after obtaining approval of QA / QC Manager:
9. Control of Nonconforming Products
To ensure that the finished quality product not conforming to requirements is identified & controlled to prevent its unintended dispatch or delivery and use on site (It is applicable to incoming material, in-process & finished products alike).
QA/QC Staff (Inspectors, Supervisors and Engineers) are responsible and accountable for reporting all nonconformities to QAIQC Manager.
10. Control of Non-conformance of Incoming Material (on shop)
If QC Dept. discovers any nonconformance through his testing, he identifies the material with “REJECTED” & records the actual status in Nonconforming Report (ISO-QP8.3.0/1 ).
11. Control of Non-conformance during Manufacture/ Production
All products in production area are considered accepted unless identified and segregated or quarantined with any sticker or mark-up.
Minor Nonconformity during manufacturing/production processes is identified on Inspection Reports & rectified by the production staff per approved repair procedure.
In case of major nonconformity, QC inspector records the nonconformity in Nonconforming Report (ISO QR8.3.0/1) & sends it to QAJQC Manager. QA/QC reviews the nonconformity & decides the disposition of the nonconformity with concerned dept. QAJQC follows the required disposition & records the results on Nonconforming Report (ISO-QP8.3.0/1 ). In case required actions are found not to reveal the desired finished product and not to provide a complete work, the process will be repeated.
12. Control of Non-conformance on Site
All Minor Nonconformity on site is rectified by the site staff prior to incorporating in the work and/or after installation or erection & fixing per approved repair procedure.
If Major nonconformity is discovered, Site in Charge or QA I QC Inspector records the nonconformity in Nonconforming Report (ISO-QR8.3.0/1) & sends it to QA/QC Manager. QA/QC in coordination with concerned department identifies the root cause, disposition & the required action on the Non-conformed product to resolve the related non conformance proposing corrective action per approved repair procedure. The corrective action shall be approved and witnessed by client.
13. Quality Records
All data and other objective evidence supporting the implementation of the quality system is recorded on a form. A form becomes a record after completing the required data and compiled and submitted to client for information, together with monthly Quality Management report.
14. Control
- Incomplete Quality Records shall be routed in accordance with the relevant Quality Procedures and shall be stored in the designated location.
- After completion, Quality Records shall be stored in the appropriate location for the defined retention period as shown in the Quality Records Log (ISO-QR4.2.4/1).
- No records shall leave Company’s premises under any conditions except under authority of General Manager and QNQC Manager other than that are to be submitted to client.
15. Disposition
• At the beginning of each year, the QA / QC & Safety Manager shall review the stored Quality Records with a view of disposition.
• Records identified for disposal shall be stamped “Obsolete” and arrangements shall be made to remove them from company’s premises if no legal requirement exists.
• Disposition of Quality Records, after retention period, shall only be done at the discretion of the QA / QC Manager.