To guide the responsible persons in conducting Current Transformer Turns Ratio Test.
Testing the current transformer (CT) ratio is essential to ensure accurate and reliable performance in power systems. The ratio test determines the transformation ratio between the primary and secondary currents of the CT. Below is a general procedure for conducting a current transformer ratio test:
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS – The following Safety precautions shall be taken in consideration prior, during and after conducting the test measurements.
- Safety tagging shall be implemented.
- Isolate the Area by Safety Warning Tape.
- Keep a Safe Distance from the device being tested.
- Wear Appropriate Personal Protective Equipment(PPE) Prior to starting any testing activity.
- Implementation of Proper Grounding.
Current Transformer Ratio Test Procedure
- Setup the CALIBRATED test instrument in a firm, reasonably level base and dry area.
- Identify test parameters and terminals for proper connections.
- The CT must be in de-energized condition and completely isolated from other energized circuit.
- For system-installed unit, isolate the burden (cable run to control room).
- Set-up and effectively ground the test instrument. Supply voltage, 110Vac or 230Vac. Conduct testing as per the following illustrated test Connections:
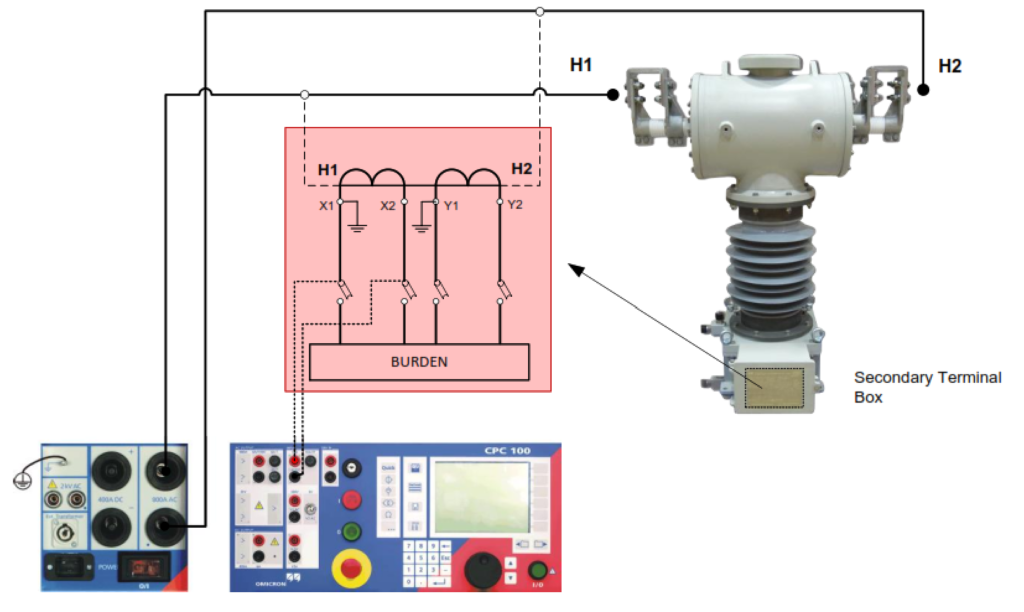
- Power ON the Test Instrument and select CTRatio Test Card
- Properly fill-up test settings:
7.1 Indicate actual name-plate ratio.
7.2 Current injection up to 800A. Indicate actual primary current at Itest.
7.3 For Primary current above 800A, use any current below 800A, or use the current booster up to 2000A. - Press I/O (test start/stop) push-button to start the test.
- Save test card for printing.
9.1 For multi-tap core/s, create and save test card for each tap tested. - Note and record all necessary test parameters
- Evaluate test result as per general standard ratings and accuracy classes for current transformers
More Important Points
1. Safety Precautions:
- Follow all safety procedures, and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Ensure that the CT is isolated from the power system before conducting any tests.
2. Disconnect CT:
- Disconnect the CT from the power system or any connected equipment to ensure safety during the test.
3. Test Equipment Setup:
- Use a suitable CT ratio test set or a secondary injection kit for the test.
- Connect the test set to the secondary terminals of the CT.
4. Excitation of CT:
- Apply a low-voltage, low-frequency (typically 50 or 60 Hz) signal to the secondary winding of the CT using the test set.
- The applied signal should be within the CT’s rated burden and be sufficient to produce a measurable output.
5. Measure Primary and Secondary Currents:
- Measure the primary current (I1) and secondary current (I2) using the test set.
- Ensure that the current measurements are accurate and within the limits of the test equipment.
6. Calculate Ratio:
- Calculate the transformation ratio (N) using the formula: N = I1 / I2.
- Compare the calculated ratio with the CT’s rated ratio specified by the manufacturer.
7. Acceptance Criteria:
- Verify that the calculated ratio falls within the acceptable range specified by the manufacturer or industry standards.
- Typically, the acceptable deviation from the rated ratio is defined in percentage terms.
8. Polarity Check (Optional):
- Optionally, perform a polarity check to ensure that the CT’s primary and secondary windings are connected in the correct polarity.
- Incorrect polarity can be identified by observing a 180-degree phase shift between the primary and secondary currents.
9. Record and Report:
- Document all test results, including the measured currents, calculated ratio, and any relevant observations.
- If the CT ratio deviates from the specified limits, further investigation and corrective actions are necessary.
10. Reconnect CT:
- After completing the ratio test and ensuring that the results are satisfactory, reconnect the current transformer to the circuit.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s documentation for specific guidance on conducting ratio tests for a particular current transformer model. Additionally, adhere to safety guidelines and regulations during the testing process. If you are not experienced in performing these tests, consider seeking assistance from qualified personnel.