DC hi-pot testing of medium voltage (5kV-35kV) power cables is a critical procedure used to check the insulation integrity and reliability of the cables under high voltage conditions. This testing is essential to ensure the safety and performance of electrical power distribution systems.
In this article, we will explore the purpose of DC hi-pot testing, the testing procedure, safety considerations, and its importance in maintaining medium voltage power cable.
DC Hi-Pot Testing of Medium Voltage Cable.
- Only qualified employees are allowed to perform high voltage test or work.
- High voltage cables shall be DC high-potential tested in accordance with SAES-P-104 Para. 13.
- This DC hi-pot testing applies to cable voltage rated 5kV and above. Refer to below table 3.
- Prior to DC hi-pot testing, perform cable continuity and phasing check for each cable.
- Check the insulation resistance of the cable using 5000 volts DC megger tester. The insulation resistance of each core should be checked to ground and between cores.
- All permanent and consumable materials shall be prepared prior to testing.
- Manpower, equipment, tools, and other logistics shall be prepared and ready for installation.
- Prepare the workplace such as barricading the area and housekeeping.
- Electrically hazardous task plan / permit shall be completed and signed before any work proceeds.
DC Hi-Pot Testing Procedure.
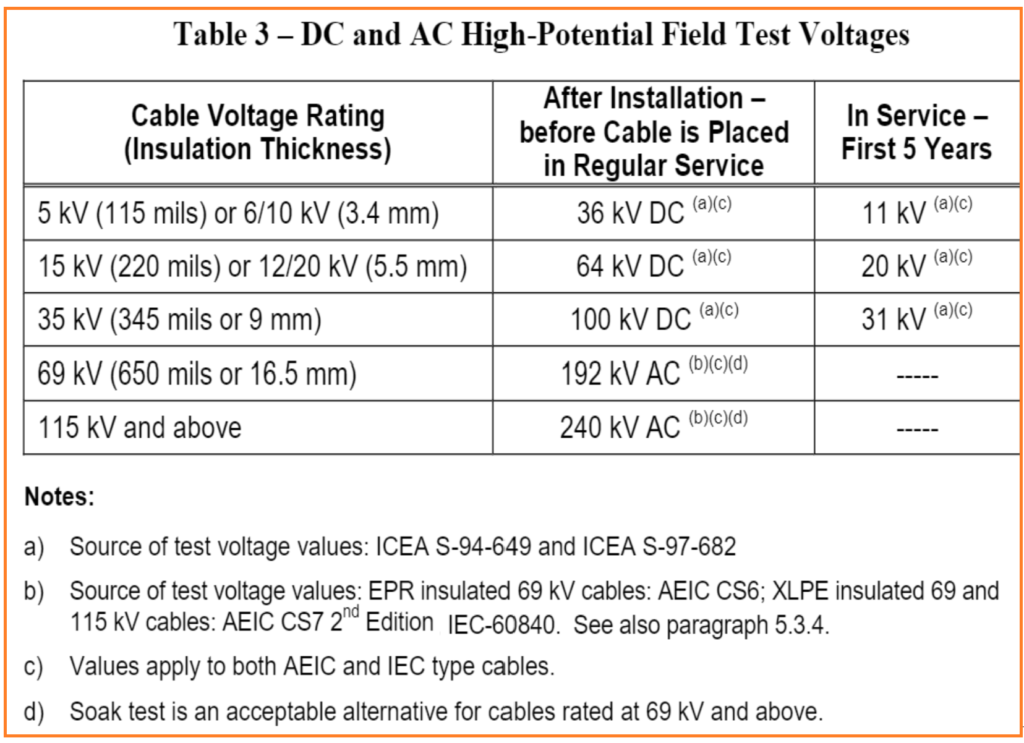
Below diagram is showing equipment arrangement of DC Hi-Pot Testing of medium voltage cable.
- Switch the MAIN BREAKER ON of the test equipment. The AC ON lamp will light.
- Close external interlock switch, if used.
- Push the HV ON push button. The HV ON lamp will light. The VOLTAGE CONTROL must be at 0 (RESET) for the HV ON push button to operate. CAUTION: The unit is now capable of producing high voltage at the OUTPUT.
- Advance the VOLTAGE CONTROL slowly until the desired test voltage is read on the OUTPUT VOLTAGE kilo-volt meter.
- Maintain the test voltage for 15 minutes. The OUTPUT CURRENT meter indicates the leakage current of the specimen under test. Select appropriate current range. See manufacturer’s instruction manual for notes on interpretation of current readings. NOTE: Refer to SATR-P-3210 and SATR-P-3214 for more detailed procedure & Test Results Acceptance Criteria.
- After maintaining test voltage for 15 minutes, turn the VOLTAGE CONTROL, slowly, in the counterclockwise direction to 0 (RESET).
- Press the HV OFF push button, or open the external interlock switch.
- Allow sufficient time for the specimen charge to bleed off, which is indicated when the kilo-volt meter reading returns to zero.
- Switch MAIN BREAKER off. WARNING: The specimen under test may retain a lethal electrical charge even when the test set is turned off. The specimen must be discharged with a properly grounded grounding stick. Keep the HV terminal of the specimen and the test set’s output cable grounded at all times except when actually performing tests. Do not approach the HV module until ground bonds have been applied.
- Results shall be filed and recorded on applicable test form per approved SATIP.
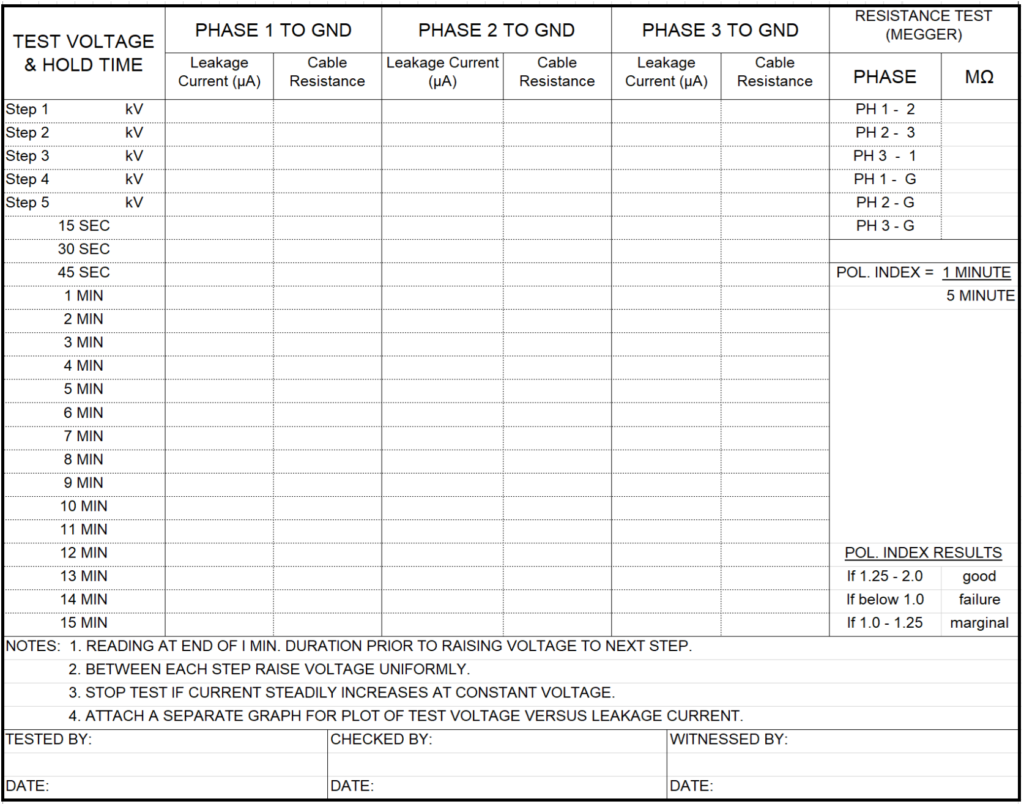
- Below is Hi Pot Test Report for MV Cable.
HV Shielded Cable Testing.
- Check the voltage rating of the cable and select the test voltage which one wants to supply for examination, refer to Table 3 above for DC High Potential Field Test Voltage.
- Start the high potential test equipment.
- The test voltage shown on Table 3 shall be reached in equal voltage and time increments. Each increase shall be made.
- Divide the test voltage rating by 5 (means 5 steps), apply the voltage slowly in a minimum of five increments until the maximum test voltage is reached.
- After each voltage increase, the leakage current shall be allowed to If the time intervals chosen are on insufficient duration to stabilize the current, the cable shall be discharged and the test repeated with new time intervals of greater, but still equal duration.
- Record the stabilized leakage current, in micro ampere, at the end of each time intervals.
- Allow the voltage to remain constant at the full test voltage and record the leakage current at 15, 30, and 45 seconds and at one minute intervals thereafter for 15 minutes for shielded cable. Compute the cable resistance using Ohm’s Law; R=V/I, where R=Resistance of Cable, V=Voltage injected, and I=Leakage current recorded.
NOTE: Plot the test voltage vs. leakage current on graph paper as the test The step voltage slope should be reasonable linear for the graphic plots.
Safety Precaution.
- Secure the approved work permit from the concerned Representative before starting any work.
- Fire Watcher with Fire Extinguisher shall be assigned at work area whenever there is hot work.
- All electrical tools shall be checked and color-coded.
- Hazardous area and its precautionary measure requirements shall be properly discussed to the working crew following all safety requirements.
- Continuous monitoring and checking shall be conducted by concerned supervisor/foreman to detect and correct unsafe practices while performing the work activities.
- Provide warning sign and sufficient barricade on working areas to avoid unauthorized entry. Only assigned personnel shall be allowed in the area.
- Safety harness with double lanyards shall be used when working at elevated temporary platforms (1.8 meters and above).
- Safety Supervisor shall monitor the work activities to help and protect all assigned workers against exposure to safety hazards. He shall ensure that Personal Protective Equipments (PPE’s) are being supplied and used and shall comply with Contractor and client applicable general instruction and standards.
- Toolbox meeting shall be conducted by Electrical Supervisor daily so that work activities will be properly coordinated to all concerned and all safety measures will be carried out on the entire work duration.
- Housekeeping shall be maintained and working area shall be kept clean and tidy in accordance with Site Housekeeping Procedure.
- Job Hazard and Risk Assessment of this procedure shall be disseminated and explained to workers for safety awareness.
Tools & Equipment Required for Hi-Pot Test.
Tools and equipment needed should be in good condition and must be checked by Supervisor / Safety Engineer prior to use in the construction area. These includes but not limited to:
- Boom Truck.
- Electrical Hand Tools.
- High Voltage Module.
- Control Unit.
- Ground Leads.
- High Voltage Output Cable.
- Interconnection Cable.
- Kilovoltmeter.
- Term Shield Conn.
All tools utilized in a classified area should be intrinsically safe and suitable for hazardous areas.
Industry Codes and Standards.
NFPA70 – National Electrical Code.
Importance of DC Hi-Pot Testing.
- Quality Assurance: DC hi-pot testing helps ensure the quality and reliability of medium voltage power cables, identifying any defects or weaknesses in the insulation that could compromise performance or safety.
- Preventive Maintenance: Regular testing of medium voltage power cables allows for early detection of insulation degradation or damage, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing the risk of electrical failures.
- Compliance: DC hi-pot testing is often required to meet industry standards, regulatory requirements, and customer specifications for medium voltage power cable installations.
- Safety: By identifying potential insulation defects or weaknesses, DC hi-pot testing helps prevent electrical faults, arc flash incidents, and other safety hazards associated with medium voltage power cable systems.
Guess I will just book marк this page.