An electrical load schedule is a engineering document that provides detailed information about the electrical loads within a facility or system. It typically includes a list of all electrical equipment, devices, and appliances connected to the electrical system, along with their corresponding electrical characteristics and operational requirements. The load schedule serves as a reference for designers, engineers, and maintenance personnel involved in the planning, design, installation, and maintenance of electrical systems.
Electrical Load Schedule Preparation
Preparing a load schedule is crucial for electrical engineers. It involves calculating the appropriate sizes for conductors, overload protection, and conduits. There are various methods for electrical design, but one non-negotiable aspect is adhering to code requirements.
Sample Electrical Plan:
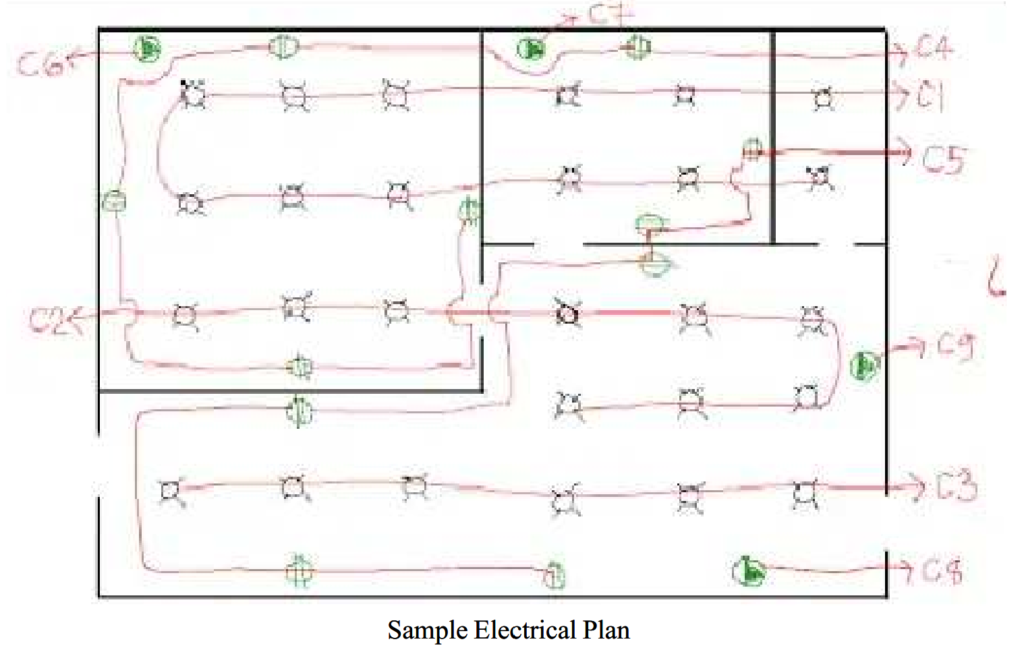
The diagram provided above serves as a simple example of an electrical plan, indicating the known number of outlets for lighting and convenience. It highlights the procedural aspect rather than replicating the actual loads of a residential unit. However, it doesn’t include calculations for voltage drop or short circuit. The system voltage in this example is 220 volts line-to-neutral.
Schedule of Loads
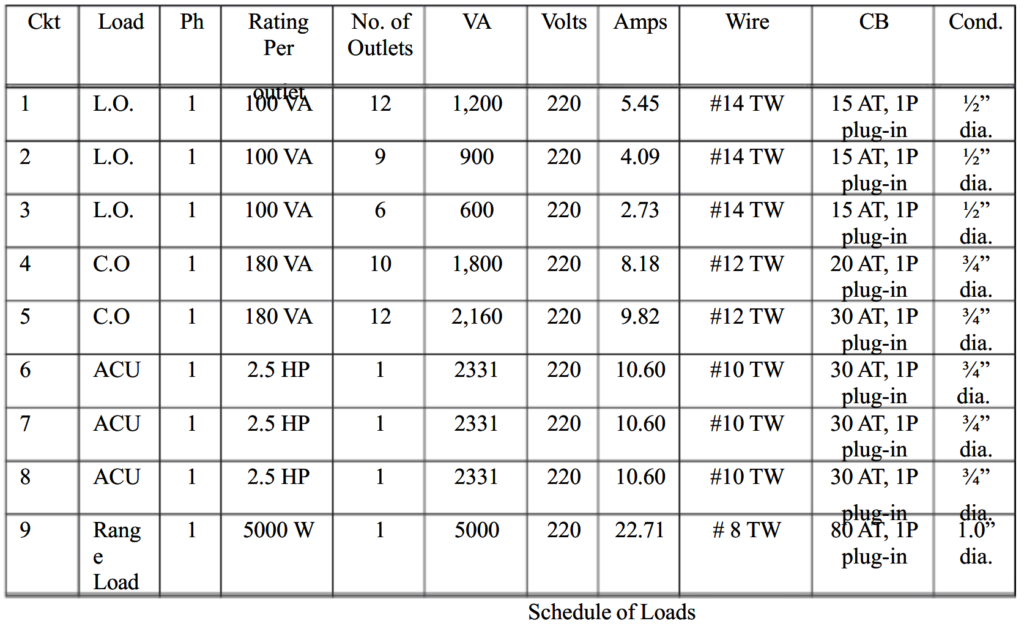
A schedule of loads is simply a summary of data aimed at easily identifying and facilitating the necessary values and equipment ratings to be used in any electrical installation. The data provided in the schedule of loads is backed by calculations based on established electrical principles and code requirements.
What Rules are Applied during preparation of Load Schedule?
- NEC 210-9a: Maximum load served by branch circuit must not be less than 80% of the ampacity of the conductor.
- NEC 430-22: The wire supplying motorized load shall not be less than 125% of the rated full load current of the motor.
- NEC 430-52: The branch circuit protection for motor loads shall not exceed 250% of motor full load current for CB and 300% for non-time delay fuses on full voltage starting.
- NEC 210-22(C): Over-Current Protection Device shall be calculated as 100% of non-continuous load + 125% of the continuous load.
Electrical Load Schedule Calculations:
Circuit 1:
- Current (I) = 1,200 VA / 220 V = 5.45 Amperes
- Wire = 5.45 / 80% = 6.82 Amperes, Use 2.0 sqmm TW wire or #14 AWG
- Circuit Breaker = Use 15 A plugin type Circuit Breaker
- Conduit = Use 1/2″ diameter PVC conduit.
Circuit 2:
- Current (I) = 900 VA / 220 V = 4.09 Amperes
- Wire = 4.09 / 80% = 5.11 Amperes, Use 2.0 sqmm TW wire or #14 AWG
- Circuit Breaker = Use 15 A plugin type Circuit Breaker
- Conduit = Use 1/2″ diameter PVC conduit.
Circuit 3:
- Current (I) = 600 VA / 220 V = 2.72 Amperes
- Wire = 2.72 / 80% = 3.41 Amperes, Use 2.0 sqmm TW wire or #14 AWG
- Circuit Breaker = 6.82 Amperes, Use 15 A plugin type Circuit Breaker
- Conduit = Use 1/2″ diameter PVC conduit.
Circuit 4:
- Current (I) = 1,800 VA / 220 V = 8.18 Amperes
- Wire = 8.18 / 80% = 10.23 Amperes, Use 3.5 sqmm TW wire or #12 AWG
- Circuit Breaker = 20.45 Amperes, Use 20 A plugin type Circuit Breaker
- Conduit = Use 3/4″ diameter PVC conduit.
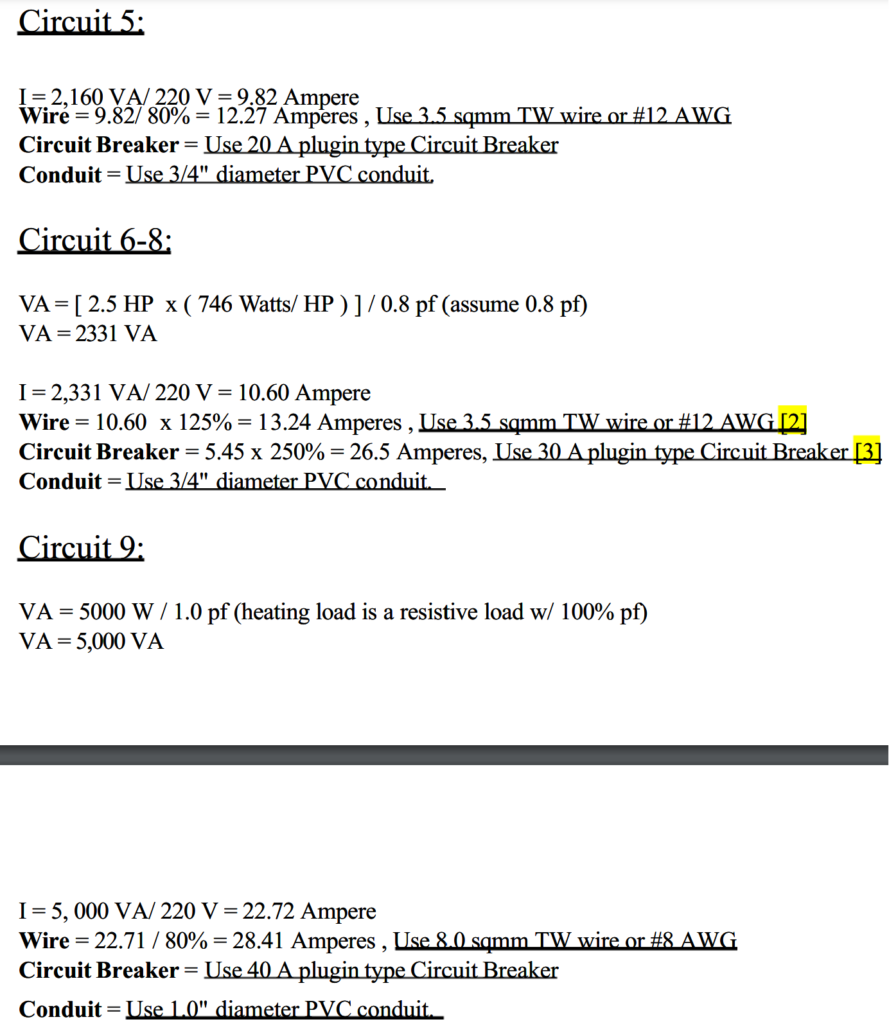
Main Feeder Analysis: By inspection:
- Continuous loads = 9,963 VA or 45.29 A at 220V (lighting loads and ACU)
- Non-Continuous = 8,960 VA or 40.72 A at 220V (conv. outlet & range load)
- Total Loads = 19,923 VA
Main Feeder Current Calculation: Main Feeder Current = (45.29 A x 100%) + (40.72 A x 125%) = 96.19 Amperes
Recommended Specifications:
- Use 50 sqmm TW cable as the main feeder or service entrance wire.
- Use a 100 Ampere MCCB, 1 pole – 10 KAIC* (*Note: 10 kAIC is an assumed value; short circuit calculation is needed to determine the right specs of the OCPD in this example)
1. What is an electrical load schedule?
2. Why is an electrical load schedule important?
3. What information is included in an electrical load schedule?
4. How is an electrical load schedule prepared?
5. What standards and regulations govern the preparation of an electrical load schedule?
National Electrical Code Book.
Electric Circuit Breaker Catalogue.