When it comes to designing and constructing piping systems, selecting the appropriate materials for flanges is a crucial step. Flanges serve as integral components that connect and seal various sections of the piping network. Ensuring compatibility, reliability, and safety requires careful consideration of material specifications. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of flange material selection and the standards that govern this process. Here we discussed technical specification of flange materials, Weld Neck Flanges, Blind Flanges and flange materials as per API SPEC 6A.
Flange Material Technical Specifications
Compatibility with Pipe Material
First and foremost, the chosen flange material must be compatible with the pipe material for the specific service the piping system is intended for. Compatibility ensures that the materials can withstand the intended pressure and temperature conditions. The pressure and temperature ratings should align with the dimensional standards applicable to the flanges.
Weld Neck Flanges
Weld neck flanges are commonly used in piping systems. For carbon steel and alloy steel flanges, the material specifications must adhere to 02-SAMSS-011. Other materials should follow the relevant ASTM standards. Here are some specific considerations:
- Carbon Steel Flanges: Refer to above Table of the standard to select the appropriate ASTM specifications for flange class ratings ranging from 150 to 1500.
- Equal Yield Strength: Ideally, the flange and the pipe should have equal yield strength. However, in cases where they do not match, some exceptions may apply. For example:
- Flanges under material group number 1 may be used with grade X42 or X52 pipes up to specific sizes.
- Flanges under material group number 2 may be used with grades X42, X52, X65, and X70 pipes.
- Flanges under material group number 3 may be used with grade X70 pipes.
- Flanges under material group number 4 may be used with grade X70 pipes.
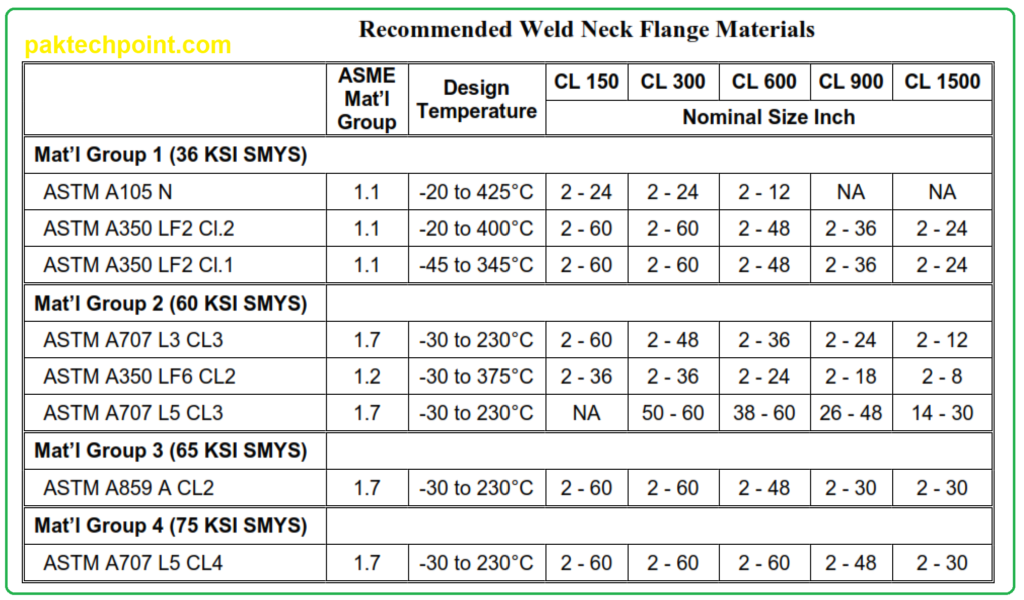
1) All 02-SAMSS-011 materials may be used wet sour service. Unless otherwise specified, manufacturers may substitute materials within limits described in 02-SAMSS-011 paragraph 4.3.
2) NA = not applicable; NR = not recommended.
3) ASME/ANSI ratings are only valid at temperatures shown above.
It’s important to note that the design wall thickness for the flange should meet the pipe’s design conditions at the butt weld joint, and the flange wall thickness will typically be greater than that of the pipe.
- Low Alloy and Stainless Steel: ASTM A182 is the appropriate choice for low alloy and stainless steel flanges. Both the flange and the pipe material’s chemical composition should match.
Blind Flanges
Blind flanges, commonly used in ASME flanges, have specific material requirements based on temperature ranges:
- A105N: Suitable for temperatures from -20°C to 425°C.
- A350 LF2 Cl 1: Suitable for temperatures from -45°C to 425°C.
- A516 Gr 70 N: Suitable for temperatures from -45°C to 425°C.
API SPEC 6A
For piping systems that adhere to API SPEC 6A, materials should align with 02-SAMSS-011 and Table 4 of the API specification. ASTM A707 L3 CL3 QT is recommended for welding neck flanges and blind flanges in these systems.
In conclusion, selecting the right materials for flanges is a critical aspect of ensuring the reliability and safety of piping systems. Compatibility with pipe materials, adherence to industry standards, and consideration of temperature and pressure conditions are all vital factors in this process. Proper material selection contributes to the overall integrity and performance of the piping network.