A slip ring motor, also known as a wound rotor motor, is a type of induction motor with some distinctive features compared to standard squirrel cage induction motors. The key difference lies in the rotor construction and the means of providing electrical connection to it.
Keep in Mind: Slip ring motor is a type of asynchronous motor. For basic details of slip ring motor please check out this article.
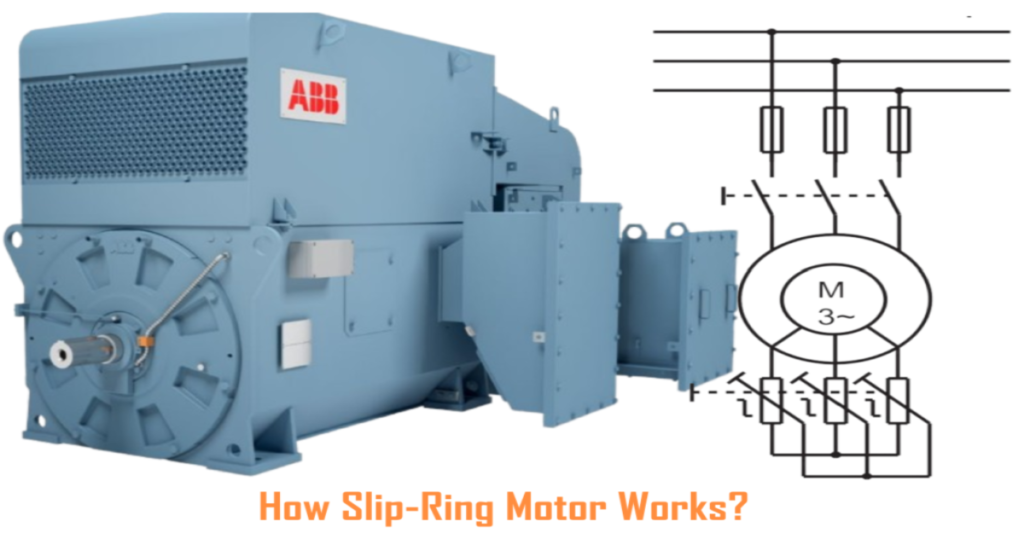
How Slip Ring Motor Works?
Slip-ring motors use a different method for controlling starting torque compared to standard induction motors. In slip-ring motors, the rotor winding is connected to slip rings, allowing for the addition of external resistances. These external resistors influence the current flowing through the rotor and consequently affect the speed-torque characteristic of the motor. Below diagram of a slip-ring motor with external rotor resistances.
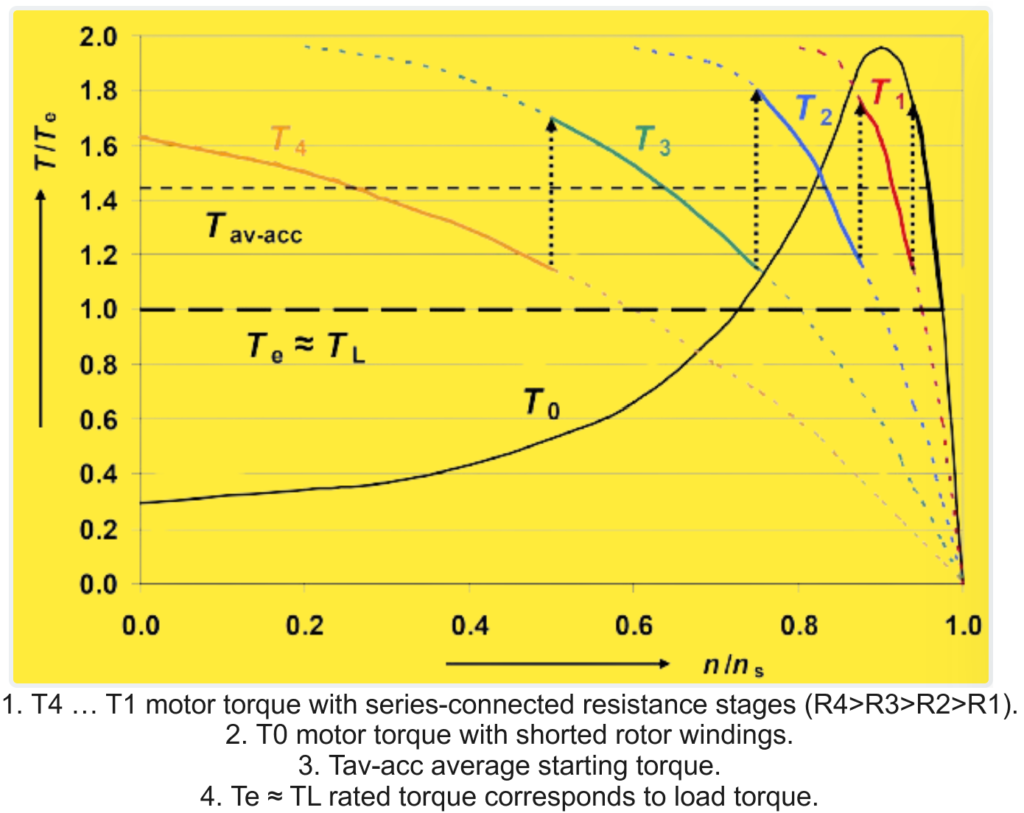
The traditional way of controlling starting torque (and current consumption) in slip-ring motors is by selecting appropriate rotor resistances. Interestingly, the highest achievable starting torque corresponds to the motor’s breakdown torque, regardless of the magnitude of the rotor resistance. This means that even with different resistance values, the motor can reach its maximum starting torque potential.
The primary current consumption in slip-ring motors is directly proportional to the rotor current. This characteristic allows slip-ring motors to achieve high starting torque with relatively low current consumption compared to other motor types. Therefore, slip-ring motors are favored for applications requiring high starting torque and efficient operation.
The method of controlling the speed of slip-ring induction motors during startup by changing the external resistors. Slip-ring motors are a type of induction motor designed to provide better control over speed and torque characteristics compared to standard squirrel-cage induction motors.
How Slip Ring Motor can Control the Speed?
Follow the below key points.
- Startup Process: During startup, external resistors are used to control the flow of current to the rotor windings. These resistors are typically changed in steps, meaning they are adjusted gradually to allow the motor to accelerate smoothly. This stepwise adjustment helps prevent excessive current surges and mechanical stresses on the motor.
- Rotor Windings: In normal continuous duty operation, the rotor windings of slip-ring motors are shorted. This means that the rotor windings are electrically connected in a closed loop, allowing current to flow through them and inducing a magnetic field that interacts with the stator field to produce torque.
- Rotor Resistance Design: The rotor resistances are designed for continuous duty, meaning they are selected to handle the heat dissipation generated during normal motor operation. By designing the rotor resistances for continuous duty, it becomes possible to continuously influence the speed of the motor. However, this comes at the cost of high heat dissipation due to the increased resistance in the rotor circuit.
- Torque Characteristic: During startup, the torque characteristic of a slip-ring motor with full-load startup and stepped changes in rotor resistance allows for smooth acceleration. By adjusting the rotor resistance, the torque-speed curve of the motor can be tailored to meet specific application requirements. This control over torque and speed enables slip-ring motors to be used in applications where precise speed control is necessary, such as in cranes, hoists, and conveyor systems.
Overall, the importance of external resistors in controlling the startup and speed characteristics of slip-ring motors, emphasizing their ability to provide smooth acceleration and precise speed control in various industrial applications.
Components of Slip Ring Motor.
There are following parts or components of slip ring motor.
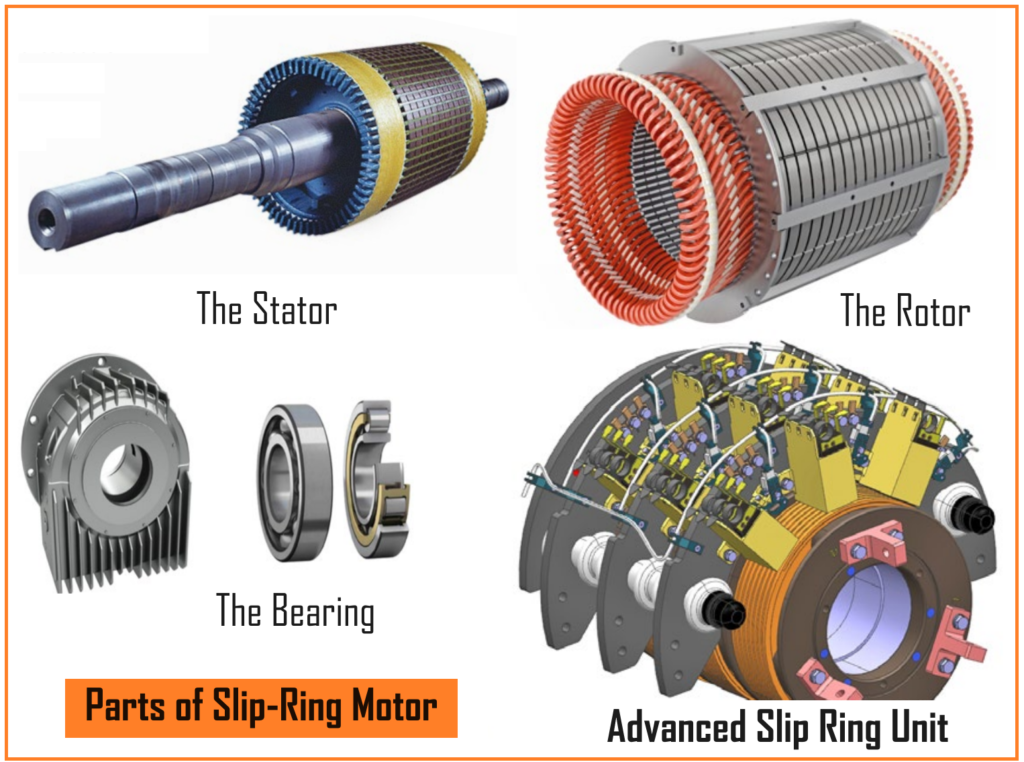
The Rotor.
The rotor of a slip ring motor, also known as a wound rotor, is a critical component that distinguishes it from standard squirrel cage induction motors.
The Stator.
The stator is another essential component of a slip ring motor, as well as of most electric motors. It’s the stationary part of the motor and surrounds the rotor.
The Bearing.
Bearings are crucial components in electric motors, including slip ring motors. They support the rotor shaft, allowing it to rotate smoothly within the stator.
Advanced slip ring unit.
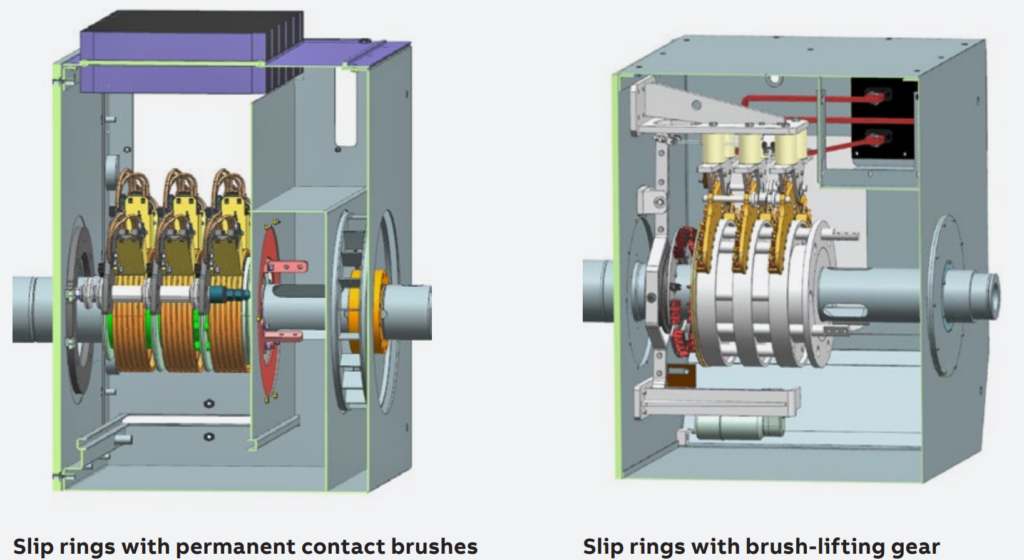
The advanced slip ring unit for wound rotor motors offers two main options for supply: permanent contact brushes or brush-lifting gear. In both cases, the slip rings are housed separately from the main motor frame, typically at the N-end. This setup facilitates easy access and maintenance, with openings that allow observation of brush operation, even in low-light conditions, thanks to installed lighting.
This arrangement effectively prevents carbon dust from entering the motor and provides flexibility in selecting different enclosures and cooling methods for the slip ring housing. Additionally, filters are installed, and these are safeguarded by a standard differential pressure switch, enhancing operational safety and reliability.
Slip rings with permanent contact brushes.
Slip rings with permanent contact brushes are made from a highly corrosion-resistant Cu-Sn-Ni alloy. They are helically grooved to ensure even wear of the brushes, which optimizes current transmission and extends brush life. This design is suitable for motors operating under demanding load cycles, ensuring long-term reliability.
Slip rings with brush-lifting gear.
On the other hand, slip rings with brush-lifting gear are constructed from stainless steel with a smooth, non-grooved surface. These slip rings are used in motors designed for continuous operation over long periods. The brush-lifting gear includes a device that raises the brushes from the slip rings after the motor reaches full speed. Before lifting the brushes, the gear short-circuits the rotor windings to ensure smooth operation during the transition.