Level switches are essential devices used in various industrial, commercial, and residential applications to monitor and control fluid levels. They play a crucial role in maintaining safe and efficient processes by alerting operators or triggering actions when a specified liquid level is reached. In this article, we will delve into the world of level switches, exploring their functionality, different types, and common applications.
Working Principle of Level Switches
Level switches, also known as liquid level sensors or level sensors, are designed to detect the presence or absence of liquids and provide an electrical or mechanical signal when a predetermined level is reached. Their primary function is to prevent overflows, maintain optimum fluid levels, and safeguard equipment from damage caused by low or high liquid levels.
The basic operation of a level switch involves a sensor element, which is positioned at a certain height within a container or tank. When the liquid level rises or falls, it triggers a response in the sensor, causing it to either open or close an electrical circuit, activate a relay, or send a signal to a control system. This signal can then be used to control pumps, valves, alarms, or other equipment to maintain the desired level.
Components of Level Switches
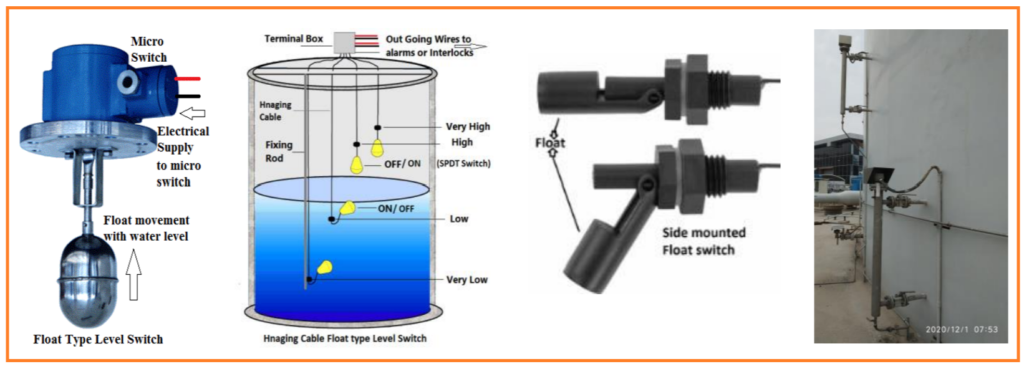
Following we summarized the components and functionality of level switches using micro switches, floats, and displacers:
- Micro Switches: Micro switches, also known as miniature snap-action switches, are compact and highly reliable electrical switches. They are commonly used in level switches due to their ability to provide a precise and rapid response when actuated. Micro switches are versatile, as they can be integrated into various level sensing mechanisms.
- Floats: Floats are buoyant devices typically made of materials like stainless steel, plastic, or foam. They are attached to a lever or cable inside a tank or vessel. As the liquid level rises or falls, the float follows suit, causing the attached lever or cable to actuate the micro switch. When the float reaches a predetermined level, it triggers the micro switch, leading to a change in the switch’s electrical state. This change in state can be used to signal an alarm, control the filling or draining of the tank, or trigger other relevant actions.
- Displacers: Displacers are often used as an alternative to floats, especially in applications involving aggressive or corrosive liquids. A displacer is typically a cylindrical or rod-shaped object made of materials resistant to the liquid being measured. Like floats, displacers are connected to a cable or rod that actuates the micro switch when the liquid level reaches a specified point. Displacers are ideal for situations where floats might not be suitable due to the nature of the liquid or environmental conditions.
Types of Level Switches
There are several types of level switches available, each tailored to specific applications and liquid types. Here are some common types:
- Float Level Switches: These switches use a buoyant float attached to a lever or cable. As the liquid level changes, the float rises or falls, actuating a switch mechanism. Float switches are widely used in sump pumps, septic tanks, and water tanks.
- Capacitance Level Switches: Capacitance level switches rely on changes in capacitance between two electrodes immersed in the liquid. When the liquid level reaches the electrodes, the capacitance changes, signaling the switch to change state. These switches are suitable for various liquids, including corrosive or viscous ones.
- Ultrasonic Level Switches: Ultrasonic level switches use sound waves to measure the distance between the sensor and the liquid’s surface. They are non-contact devices, making them ideal for applications involving hazardous or corrosive liquids.
- Optical Level Switches: Optical level switches utilize light beams to detect the presence or absence of liquid at a specific level. When the liquid interrupts the light path, the switch triggers an action. These switches are used in clean and clear liquid applications.
- Conductive Level Switches: Conductive level switches use electrical conductivity to detect the presence of liquid. When the liquid bridges the gap between two conductive probes, it completes an electrical circuit, activating the switch. These are often used in conductive liquids like water.
Applications of Level Switches
Level switches find applications in a wide range of industries and processes, ensuring safe and efficient operations. Some common applications include:
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: Level switches are used in water treatment plants to monitor water levels, control pumps, and prevent overflows in tanks and reservoirs.
- Oil and Gas Industry: They are employed in oil refineries and storage tanks to manage liquid levels, detect leaks, and prevent spills.
- Food and Beverage Processing: Level switches are used to maintain consistent ingredient levels, manage product flow, and prevent overfilling or underfilling in production processes.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: In pharmaceutical facilities, level switches help control the levels of various liquids used in drug production and packaging.
- HVAC Systems: They are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to monitor condensate levels and prevent flooding.
- Industrial Automation: Level switches play a critical role in automating industrial processes, such as filling, mixing, and batching operations.
Conclusion
Level switches are indispensable devices that ensure the proper management of liquid levels in a wide array of applications. By detecting changes in liquid levels and triggering appropriate actions, they help maintain safety, efficiency, and the integrity of equipment and processes. The choice of the right level switch depends on factors like the type of liquid, application, and environmental conditions, ensuring that these devices continue to play a vital role in various industries worldwide.
Read Full Course on Instrumentation and Control Engineering.