LORAN-C, which stands for Long Range Navigation-C, is a terrestrial radio navigation system developed to provide accurate positioning information for ships and aircraft over long distances. It works by measuring the time difference between radio signals received from multiple ground-based transmitters known as LORAN stations.
What is LORAN-C?
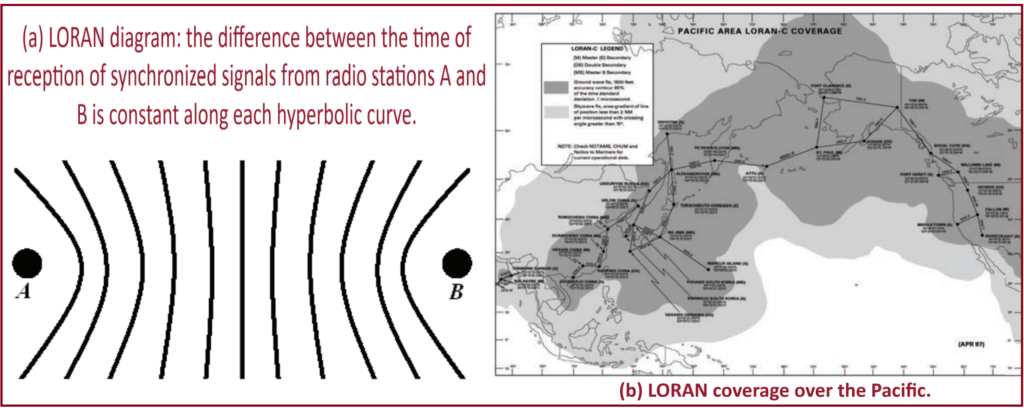
LORAN-C, or Long Range Navigation-C, is an advanced navigation system comprised of a network of stations that utilize low-frequency radio signals to provide extensive coverage. It represents an evolution from its predecessor, Loran-A, which was developed during World War II. LORAN works by measuring the time difference between signals received from pairs of radio transmitters. This time difference, when constant, corresponds to a hyperbolic line of position.
By knowing the positions of the synchronized stations and identifying the hyperbolic curves with constant time differences, the position of an aircraft can be determined. In ideal conditions, this method is equivalent to calculating the difference in distances from the aircraft to each of the two stations. By triangulating these signals, LORAN-C can determine a user’s position with a high degree of accuracy, typically within a few hundred meters to several kilometers.
LORAN-C was widely used before the advent of GPS (Global Positioning System) and provided reliable navigation capabilities, especially in areas where GPS signals might be degraded or unavailable. However, with the widespread adoption of GPS technology, LORAN-C has largely been phased out in favor of more modern and accurate navigation systems.
How LORAN-C Works?
To accurately determine its position, an aircraft needs signals from at least three LORAN transmitter stations. By comparing the time differences between signals received from different pairs of stations, the aircraft can calculate its position relative to each station. This information creates intersecting hyperbolic lines, which pinpoint the aircraft’s location.
LORAN has historically been crucial for navigation over large bodies of water, such as oceans, where other navigation systems like VOR and DME may not provide adequate coverage. However, with the advent of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) like GPS, LORAN usage has declined significantly. Nevertheless, LORAN still holds relevance as a backup navigation system and as an alternative in areas where GNSS signals may be unreliable or unavailable due to factors like interference or signal blockage. Efforts to modernize and enhance LORAN continue, aiming to maintain its utility in supporting safe and reliable navigation for aviation and maritime purposes.