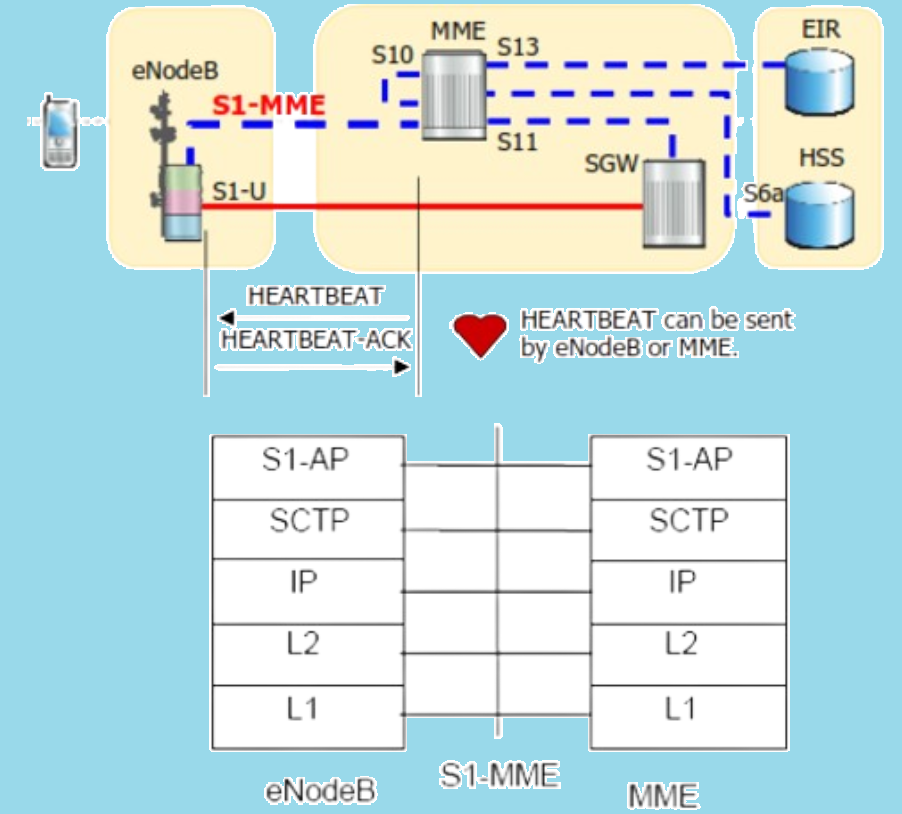
The S1-MME interface is a critical control plane interface in LTE networks, connecting the evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (eUTRAN) to the Mobility Management Entity (MME). This interface ensures effective communication and coordination between the base stations (eNodeBs) and the MME.
S1-MME Interface Protocols.
- S1 Application Protocol (S1-AP)
- Layer: Application Layer.
- Function: Facilitates communication between eNodeB and MME.
- Standard: Defined in 3GPP TS 36.413.
- Procedures: Includes setup, modification, and release of bearers, handovers, and paging coordination.
- Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP)
- Layer: Transport Layer.
- Function: Ensures reliable delivery of signaling messages between eNodeB and MME.
- Setup: eNodeB initiates the connection and sets up an SCTP association with all MMEs in its assigned MME pool.
SCTP Implementation.
- Connection Initiation:
- The eNodeB initiates the SCTP connection upon startup or restart.
- MME accepts the connection based on provisioned eNodeB IP addresses.
- After the SCTP connection is established, the eNodeB sends an S1 setup message to exchange necessary data with the MME.
- Reliability Features:
- Heartbeat Function: Ensures the connection is always monitored and maintained.
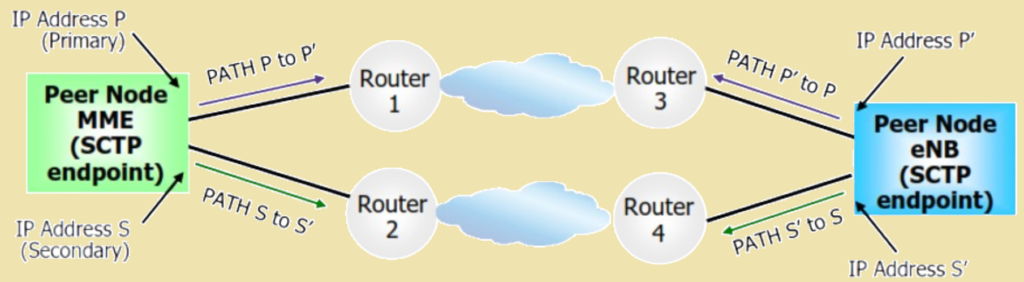
- Multi-homing Support:
- Allows multiple SCTP paths between eNodeB and MME for increased reliability.
- Supports up to two IP addresses per SCTP endpoint (primary and alternate), enhancing redundancy.
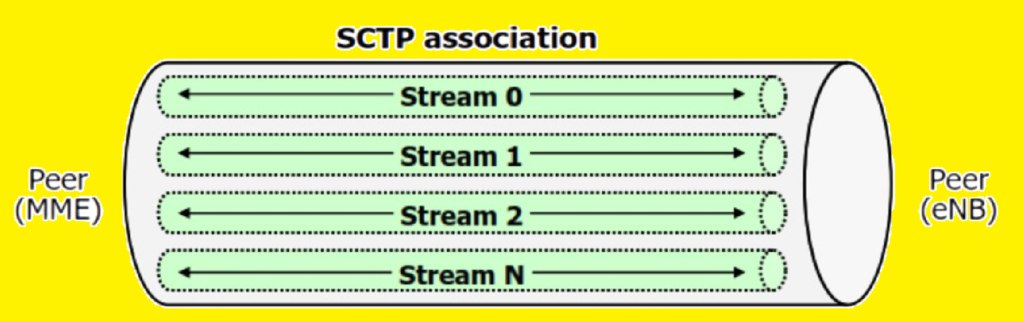
- Multi-streaming:
- Streams: Supports multiple streams to separate different types of messages.
- Stream 0: Non-UE related S1-AP messages.
- Stream 1: UE-related S1-AP messages.
- Benefit: Loss in one stream does not affect the other streams, maintaining efficient message delivery.
- Streams: Supports multiple streams to separate different types of messages.
SCTP Multi-Homing and Multi-Streaming.
Multi-Homing:
- Configuration: MME is configured with multiple IP addresses (IPv4 or IPv6).
- Redundancy: Each path uses a different physical port, with the SCTP protocol managing redundancy.
- Heartbeat Support: Active on both primary and alternate paths, ensuring continuous monitoring.
- Alarms: Triggered if a path becomes unavailable or there is a mismatch in provisioning data.
Multi-Streaming:
- Data Partitioning: Data is divided into multiple streams, each independently sequenced.
- Transport Efficiency: Uses a common flow and congestion control mechanism, reducing overhead.
- Application: Automatically applied on S1, SGs, and SBc interfaces, with provisionable streams on the S6a interface.
Additional Functionalities.
- Paging: MME uses the S1-MME interface to page UEs in the idle state.
- Bearer Management: Manages the setup, modification, and release of bearers for data traffic.
- Handover Coordination: Facilitates seamless handovers between eNodeBs.
- Signaling Transport: Ensures reliable delivery of signaling messages crucial for network operations.
In summary, the S1-MME interface in LTE is essential for efficient control plane communication between eNodeBs and the MME. It leverages protocols like S1-AP and SCTP to ensure reliable, efficient, and secure signaling, supporting the robust performance of LTE networks.