This electrical commissioning procedure and technical specification provide a comprehensive framework for commissioning and maintaining uninterruptible power systems (UPS), batteries, and chargers. The scope of this specification encompasses visual and mechanical inspections, as well as electrical and functional testing of these critical components. It outlines the necessary procedures and practices to ensure the reliable operation of UPS systems and associated equipment.
Electrical Commissioning and Start-up Checklist
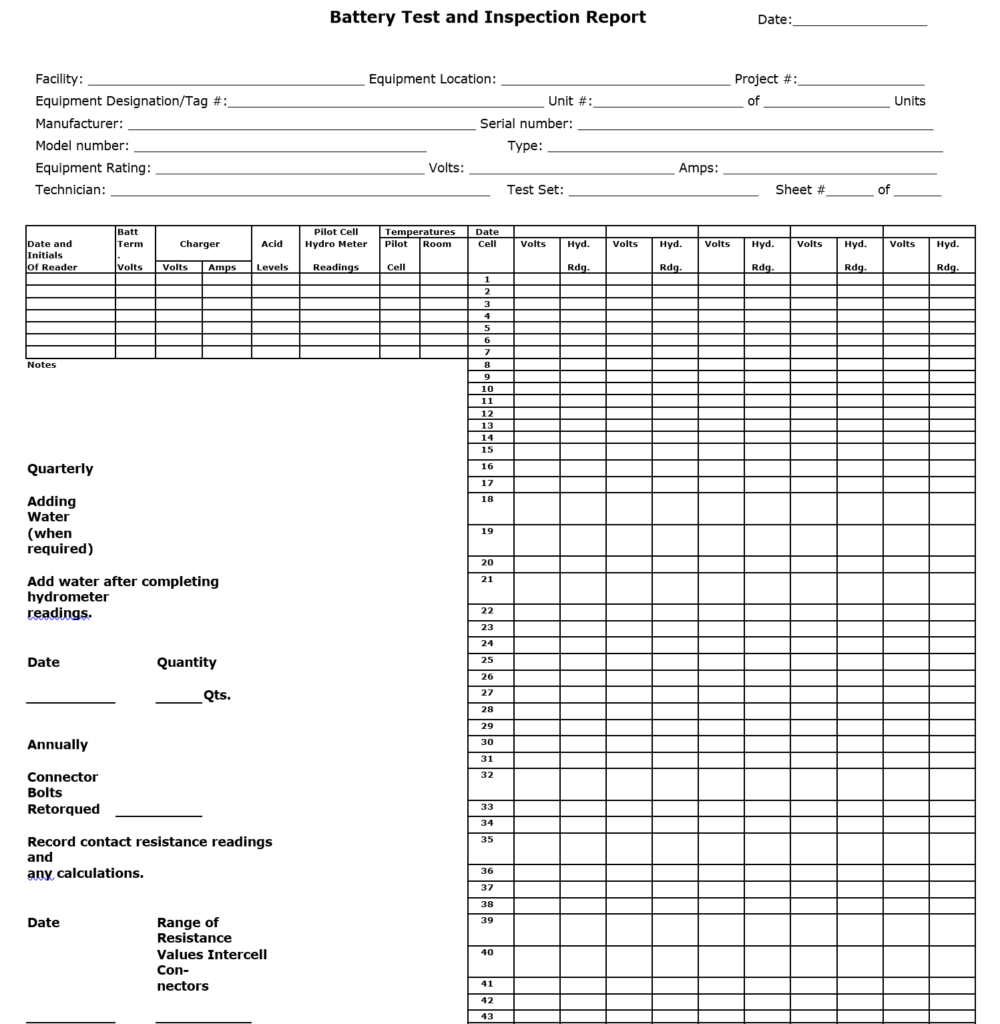
Uninterruptible Power Systems Batteries and Chargers Nameplate Data
Date:_________
Facility:_______________ Equipment Location:_________________ Project #: _____________
Equipment Designation:_________________________ Unit # _______ of _______ Units
Manufacturer:__________________________ Serial number:_______________________
Model number:________________________ Type:_______________________________
Equipment Rating:____________________ Volts:_______________ Amps:______________
Technician:______________________ Test Set:_______________ Sheet # ____ of ____
Uninterruptible Power Systems (UPS)
- Upon receipt of the equipment, inspect it for any physical damage resulting from shipping. Any such incidents should be reported in accordance with the shipper’s instructions.
- Compare the equipment’s nameplate information with the latest single-line diagram and equipment specifications to ensure alignment and accuracy.
- Ensure that the batteries are correctly installed and placed on charge immediately upon receipt.
- Verify that the batteries have proper voltage levels and maintain appropriate electrolyte levels.
- Check the specific gravity of each battery cell, if applicable, and compare it to the manufacturer’s specified data.
- Verify the proper operation of the UPS system, including its synchronization with the alternate power supply and the ability to return to normal operation. Refer to the manufacturer’s instruction literature for guidance on proper operation.
- Conduct a function test on all alarm and indicating devices to ensure they are functioning as expected.
Batteries and Chargers
- Upon receipt of the equipment, inspect it for any physical damage resulting from shipping. Any such incidents should be reported following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Compare the equipment’s nameplate information with the latest single-line diagram and equipment specifications to ensure alignment and accuracy.
- Ensure that both the batteries and charger are correctly installed and placed on charge immediately upon receipt.
- Check for proper connections and cleanliness of the batteries to ensure they are functioning optimally.
- Use a voltmeter to check for proper voltage and polarity in the battery system. The total voltage should read approximately twice the number of cells. Record the results of this measurement.
- Ensure that the batteries have the proper electrolyte levels to support their operation.
- For wet cell battery systems, perform specific gravity checks on each cell. For VRLA battery systems, measure cell voltages and compare them to the manufacturer’s specified data. Record the results of these measurements.
- Verify that all cells are numbered and that cell number one is designated as positive.
- Check the proper operation of the battery charger and verify the calibration of set points in accordance with the manufacturer’s instruction literature.
- Conduct a verification of the proper operation of all alarm circuits and indicating devices, referring to the manufacturer’s instruction literature for guidance.
Battery Test and Inspection Report
Related Articles:
Electrical Equipment Commissioning.
Electrical Work in Plants and Refineries and Commercial Buildings.
Electrical Safe Work Practices.