This article is about Testing, Calibration, Inspection and POP UP test of PRVs Pressure Relief Valves and PSVs Pressure Safety Valves and International Codes and standards used for it. How to make Pressure Relief Valve Calibration Certificate and what are testing requirements for PRV and PSV. Here we explained complete steps for calibration. Question asked many times for Frequency for Pressure Relief valve as per ASME Standard.
Table of Contents:
1. SCOPE
2. PURPOSE
3. REFERENCE STANDARD
4. STANDARD EQUIPMENT
5. RESPONSIBILITIES
6. TEST MEDIUM
7. UUC SPECIFICATION
8. PREPARATION OF TEST INSTRUMENT
9. TEST ACTIVITIES / PROCEDURE (INSPECTION & TESTING)
10. TESTING METHOD
11. POST TEST REQUIREMENTS
12. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
13. ATTACHMENTS
1. SCOPE
The Scope of this procedure details the visual examination of pressure relief valve, adjustment of set pressure (pop up) / seat tightness (if required). This procedure defines steps to perform testing & inspection of Safety & Pressure Relief Valves subject to the requirements.
2. PURPOSE
To improve PRVs performance by assuring that pressure relief devices will open at the specified set pressure within the tolerances set by the applicable code. To Ensure RVs remain in good physical condition and comply with all requirements of this procedure for external condition.
3. REFERENCE STANDARD
API RP 576 Inspection of Pressure-Relieving Devices
SAEP – 319 Pressure Relief Devices – Testing and Inspection Requirements
SAEP – 1132 Instructions for Using the Relief Valve Test Stand
SAES-J-600 Pressure Relief Devices.
SATIP-J-600-01 Safety Relief Valve Installation.
SAIC-J-2008 Relief Valve Testing and Calibration
SAEP-318 Pressure Relief Valve Program Authorization for Installation, Deletion and Changes.
SAEP-1134 Relief Valve Technician Certification.
Construction Safety Manual
Manufacture Instruction Manual.
NBIC Pressure Relief Device (PRD) Inspection Guide.
ABSA (Alberta Boilers Safety Association), AB-524“Pressure Relief Devices Requirements”, 2016 Edition
NB-501 National Board Certification of Pressure Relief Devices “Description of Program and Basic Requirements”
4. STANDARD EQUIPMENT
Shut off & Safety Valve Test Stand Pressure Range 0 to 3045 psi (210 bar) / (Air, Nitrogen & Water).
Shut off & Safety Valve Test Bench Pressure Range 0 to 5800 psi (400 bar) / (Air, Nitrogen & Water).
Shut off & Safety Valve Test Bench Pressure Range 0 to 10005 psi (690 bar) / (Water).
Valve Test Bench Pressure Range 0 to 9138 psi ( 630 bar ) / (Water).
5. RESPONSIBILITIES
Construction Manager
He shall implement HSE requirements for the job and shall study, analyze and schedule all construction activities with his department to include manpower and equipment line up as well as other possible resources required for the successful implementation of the construction work activities. He shall study all aspects of work procedure as per Technical Scope of Work.
Piping Supervisor
He shall be directly reporting to Construction Manager and responsible for the implementation and control of all activities as per JGC/DEC Technical Scope of Work and latest approved for construction drawings. He shall also designate a responsible staff that shall be in charge for execution of work to ensure that schedule, plans and allocations shall be followed and avoid unnecessary delays and obstructions.
Relief Valve Technician
Handle and transport RV’s carefully. Maintain RV at vertical position at all times. Using the instructions provided in the procedure, make initial visual inspection of the RV inlet and outlet for corrosion, clogging, indications of leakage, mechanical damage, wear, body damage, external corrosion, etc. Using an approved IN-PLACE testing procedure, per SAEP-319. Using an approved test stand (per SAEP-1132), perform the initial pop and leak tests per SAEP-319, perform all applicable tests, in shop or in-place, per SAEP-1133. Leak test PRV bellows and closed bonnet, where applicable, using minimum acceptance criteria in SAEP-319. Affix metal tag and seal properly per SAEP-318 after the completion of test. Maintain a history file comprises of PRV related correspondence.
QC Piping Inspector
He shall be responsible for inspection and monitoring of the work and ensure that the work is performed and properly documented in accordance with Project requirements.
Safety Supervisor
He shall be responsible for monitoring safely aspects and ensuring that the testing activity is done in accordance with JGC/DEC Safety Standard Procedure. He shall discuss with the workers the characteristics of related materials and status of work area giving reminders as an additional point to work safely.
6. TEST MEDIUM
Water
Air
Nitrogen
7. UUC SPECIFICATION
Type of Flanges : RF, RTJ, Welded, Grayloc
Threaded Type : 1/4 to 2 inches
Flange Type : 1/2 to Unlimited.
8. PREPARATION OF TEST INSTRUMENT
8.1 Prior to start the testing, the following instruction to be made:
Verify that the test instrument is clean and free from obvious damage, that it would impair its operation.
Check the test instrument comparing between its name plate details and specification, if available.
Required Compressed Air at 7 bar to run the pumps.
Availability of single phase 220 V & three phase 380 AC.
Hydraulic Oil – 68 grade – 20 liters for Hydraulic clamping pump.
Clean water – 100 liters for Hydrostatic test.
Size and Pressure rating of the valve to be tested.
Care should be taken for the maximum test pressure according to size.
Obtain the Clamping pressure from the chart provided.
Note: Refer to the Annex A, B & C for Test Instrument with Testing Details
8.2 Visual Inspection
The following points shall be visually confirmed.
External and internal surfaces of castings shall be free from harmful defects, such as blow holes, fins, sand inclusion burning and cracks.
Castings surfaces (both the exterior & interior) are free from holes, burrs, scale, cracks, etc.
Machined surfaces shall be free from harmful defects such as cutting, blow holes, etc.
Seat surfaces shall be free from blow holes and other harmful defects.
Corners and fillets without specified dimensions shall be properly chamfered or rounded.
Flow path portions shall be properly finished and cleaned.
Valve bodies shall have specified markings on the surface (trade mark, rating, size, flow direction, material identification and others.)
9. TEST ACTIVITIES AND PROCEDURE (INSPECTION & TESTING):
9.1 INSPECTION
9.1.1 Pressure Relief Valve Data
Nameplate marking or stamping of the device should be compared to stamping on the protected pressure-retaining item.
For a single device, the set pressure shall be no higher than the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) marked on the protected pressure-retaining item or system.
Verify nameplate capacity and, if possible, compare to system capacity requirements.
Check identification on seals and ensure they match nameplates or other identification (repair or reset nameplate) on the valve.
9.1.2 Condition of the Safety Relief Valve
Check for evidence if the valve is leaking or not sealing properly.
Seals for adjustments should be intact and show no evidence of tampering.
Connecting bolting should be tight and all bolts intact.
The valve should be examined for deposits or material buildup.
Evidence of rust or corrosion should be checked.
Check for damaged or misapplied parts.
If a drain hole is visible, ensure it is not clogged with debris or deposits.
Check for test gags left in place after pressure testing of the unit.
Bellows valves shall be checked to ensure the bonnet vent is open or piped to a safe location. The vent shall not be plugged since this will cause the valve set pressure to be high if the bellows
develops a leak. Leakage noted from the vent indicates the bellows is damaged and will no longer protect the valve from the effects of backpressure.
9.1.3 Inspection of the Safety Relief Valve
Inspect inlet piping and ensure it meets the requirements of the original Code of construction. Check that the inlet pipe size is not smaller than the device inlet size.
Inspect discharge piping and ensure it meets the original code of construction. Check that the discharge pipe size is not smaller than the device outlet size.
Check that the valve drain piping is open. Check drainage of discharge piping.
Check that inlet and discharge piping are not placing excessive stress on the valve body which can lead to distortion of the valve body and leakage or malfunction.
Check the condition and adequacy of piping supports. Discharge piping should be supported independent of the valve itself. Check for possible hazards to personnel from the valve discharge or discharge pipe.
Check that there are no intervening isolation valves between the pressure source and the valve inlet or between the valve outlet and its point of discharge. (Isolation valves may be permitted in some pressure vessel service. Isolation valves are not permitted for power boilers, heating boilers, or water heaters.)
9.2 TESTING
9.2.1 Test Stand Operation:
Testing facilities shall be submitted to SAUDI ARAMCO for approval prior to use. Inspection of these facilities shall be done on a separate activity.
Testing procedures for each type of PRV shall be available at the testing area at all times.
After passing the Inspection program, then it can be tested on the Test Stand.
The valve is tested according to its function by using either water or air.
Install the valve on the “Safety Relief Valve Test Bench”.
Check for proper clamping pressure on the chart provided.
When the required pressure is reached in the gauge, clamping operation is completed.
9.2.2 Testing Procedure – Water (Hydrostatic Test):
This test is to check leakage in a Valve with Water as a medium.
Prior to start of test, collect all the parameters, like Test pressure.
Clamping procedure has to follow.
After the valve is seated, select the LP Pump regulator.
Start the LP pump by regulating, until water filling starts.
Stop the LP pump. Select the HP pump or if you have an accumulator, select the accumulator.
Apply pressure from the HP pump or Accumulator.
Water pressure is witnessed in the 2 gauges located on the left side of the Test Bench.
These gauges are filled with Glycerin, to avoid sudden shock when Water pressure is relieved.
9.2.3 Testing Procedure – Air/Gas (Pneumatic Test):
This test is to check leakage in a Valve with Air / Gas as a medium.
Before start of test, collect all the parameters, like Test pressure.
Connect High pressure Nitrogen cylinder or Gas Booster to the connection provided on the left hand side of the Test Bench.
Clamping procedure has to follow.
Check the pressure of Gas Booster or Nitrogen cylinder in the gauge provided.
Observe the required pressure in the cylinders, regulate the pressure slowly to the Valve to be tested.
Air/Gas pressure is witnessed in the 3 gauges located on the right side of the Test Bench.
After test is performed relieve the pressure and remove the valve from test bench.
9.2.4 Relief Valve Pop Test:
The Relief Valve is generally mounted on the test bench and air or water pressure is increased slowly until the valve relieves.
To set the required pressure adjust the spring as per client’s required set pressure.
After the valve has been adjusted, it should be popped at least once to prove the accuracy of the setting.
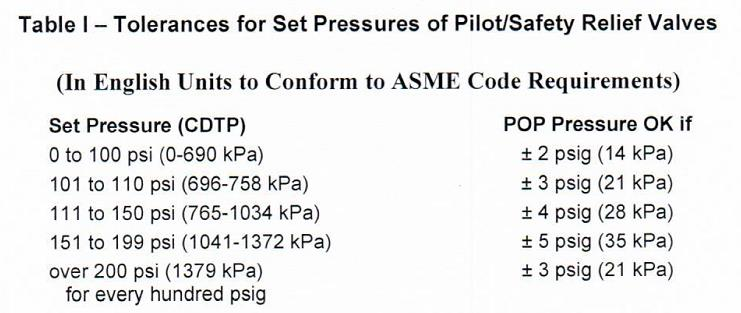
9.2.5 For Set Pressure Tolerance Reference for PRV Pop Up Test to Table I.
9.2.6 Pressure Gauge Requirements:
Pressure gauge range should be about twice the test pressure. However, in any case it shall not be lower than 1.5 times and not higher than 4 times the test pressure.
The test pressure gauge unit shall be the same unit as marked in the PRV Set Pressure.
The ranges of test pressure gauge shall be used against the RV CTPD (Relief Valve Cold Differential Test Pressure) requirement.
9.2.7 Seat Leakage Testing:
Leak Testing is conducted as required in SAEP-319. Leakage is measured through the seat to disk seal while the PRV is at 90 % of CDTP.
On the test bench, Seat Leakage Test can be performed by increasing the pressure on the valve to 90% of the CDTP and observing the discharge side of the valve for evidence of leakage.
During air test, leakage can be measured using Bubble glass apparatus. (As per in fig. Annex – D).
The rubber plug provided with test bench should be kept in the outlet of PSV.
The Bubble glass has a clear container, which should be filled with water.
Any leakage will travel from the Rubber plug through a Plastic tube into the Bubble glass.
Bubbles can be counted in the container.
Hold 90 % of CDTP for the required test period as follows:
– One minute for 0.5” to 2” RV inlet size
– Two minutes for 2.5” to 4” RV inlet size
– Five minutes for all other larger inlets sizes
Compare BUBBLES PER MINUTE leakage rate for Pilot/Safety Relief Valve to the acceptance criteria, as follows:
Ref. Table II for RV’s with CDTP up to 100 psig.
Ref. Table III for RV’s with CDTP over 1000 psig.
10. TESTING METHOD
10.1 Testing with Air / Nitrogen or a combination of Air and Liquid:
Test Medium
The test medium shall be air (or nitrogen) near ambient temperature.
Test Configuration
The valve shall be vertically mounted on the test stand, and the apparatus shall be attached to the valve outlet.
All openings – including but not limited to caps, drain holes, vents and outlets shall be closed.
Test Pressure
For a valve with set pressure greater than 50 psi, the leakage rate in bubbles per minute shall be determined with test pressure at the valve inlet held at 90 % of the set pressure.
For a valve set at 50 psi, the test pressure shall be held at 5 psi less than the set pressure. (Ref: API 527)
10.2 Testing with Water:
Test Medium
The test medium shall be water near ambient temperature.
Test Configuration
The valve shall be vertically mounted on the water test stand.
Test Pressure
For a valve with set pressure greater than 50 psi, the leakage rate in bubbles per minute shall be determined with test pressure at the valve inlet held at 90 % of the set pressure.
For a valve set at 50 psi, the test pressure shall be held at 5 psi less than the set pressure. (Ref: API 527)
10.3 Body Test:
After completion of Pop test and Seat Tightness, perform Body test.
Blind the outlet. (As per in fig. Annex – C)
Source 7 bar (100 psi) pressure from shop air.
Observe for leakages from Cap joint, Body and Nozzle joint, Body and Bonnet joint and whole body casting.
If found leakage in Body joints, release pressure and tighten them.
Check out this article also: Relief Valves | Sizing, Design, Purchase, Testing, Inspection and Installation
11. POST TEST REQUIREMENTS:
Reporting
Generate a final report for Inspection and testing of Relief Valve with the manufacturer specification and test results. Refer the Annex.
RV Number Stamping and Tagging:
Tag and seal the RV when the Inspection & Testing is complete. The seal shall be applied immediately upon final setting. The seal shall be a wire lock that must be broken to alter the pressure setting.
Attach the Identification Tag with RV number, Inspection & Test Date, next Inspection & Test date and test pressure to the RV.
12. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
Every person involved in operating the test stand must have read & understood the safety instructions.
When the machine is used by someone who is not trained, when improper use is made on the machine. The consequences of improper operation of the machine, in particular the negligence of the safety regulations are:
-
- The danger of injury
- Risk of damage to the machine and the operator’s property
The user is obliged only to operate the machine if it is in perfect condition.
Before each start-up, the machine is to be checked for externally identifiable damage & defects.
Pay attention to all safety and risk signs and keep them in a completely readable condition.
The operator must ensure before testing that the UUC is completely free of fault. The UUC must not be tested if that is not the case.
Moving parts must not be touched, contact with moving parts could result in serious injury.
The system may be operated only with sufficient lighting in accordance with the local stipulations.
The personnel must not keep long hair, must not wear loose and / or free-flowing clothes or jewelry including rings. There is a risk of injury as one could example get clutched, caught, entangled or pulled in.
It is absolutely necessary that goggles be put on while working in close proximity to the machine during processing.
It is absolutely necessary that safety-boots be put on while handling the machine.
Annex-A – Shut off & Safety Valve Test Bench ( Pressure Range 0 to 10005 psi (690 bar )
Valves Testing: All types of Valves
For Safety Relief, Control & Shut off Valves: The valve is clamped directly to the test port.
For Oversize Valves: Both side of the valves is fitted with Blind Flange of relevant rating and required pressure to be applied from main unit and it’s not required any separate manifold or relief valve.
No. of Valves more than one: At the time of 4 or 5 valves to be fitted with required bolt, nut, gasket at one time and both end of the valves is fitted with Blind Flange of relevant rating and required pressure to be applied from main unit and it’s not required any separate manifold or relief valve.
Annex-B – Shut off & Safety Valve Test Bench (Pressure Range 0 to 3045 psi (210 bar))
Valves Testing: All types of Valves
For Safety Relief Valve: The valve is clamped directly to the test port.
For Control & Shut off valves: The valve is clamped from the inlet on the test port and the outlet of the valves is fitted with Blind flange of relevant rating and it’s not required any separate manifold or relief valve.
For Oversize Valves: Both side of the valves is fitted with Blind Flange of relevant rating and required pressure to be applied from main unit and it’s not required any separate manifold or relief valve.
No. of Valves more than one: At the time of 4 or 5 valves to be fitted with required bolt, nut, gasket at one time and both end of the valves is fitted with Blind Flange of relevant rating and required pressure to be applied from main unit and it’s not required any separate manifold or relief valve.
Annex – C – Valve Test Bench Pressure Range 0 to 9138 psi (630 bar)
Valves Testing: All types of Valves
For Safety Relief Valve: The valve is clamped directly to the test port.
For Control & Shut off valves: The valve is clamped from the inlet on the test port and the outlet of the valves is fitted with Blind flange of relevant rating and it’s not required any separate manifold or relief valve.
For Oversize Valves: Both side of the valves is fitted with Blind Flange of relevant rating and required pressure to be applied from main unit and it’s not required any separate manifold or relief valve.
No. of Valves more than one: At the time of 4 or 5 valves to be fitted with required bolt, nut, gasket at one time and both end of the valves is fitted with Blind Flange of relevant rating and required pressure to be applied from main unit and it’s not required any separate manifold or relief valve.
Annex – D – Pictures of Relief Valve Testing using Test Bench